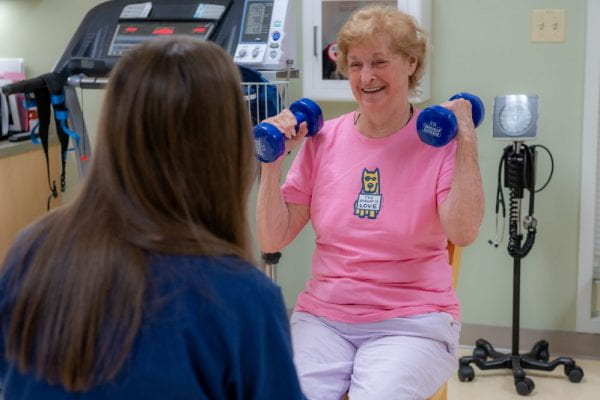Research study conducted to improve outcomes after hip fracture for older women
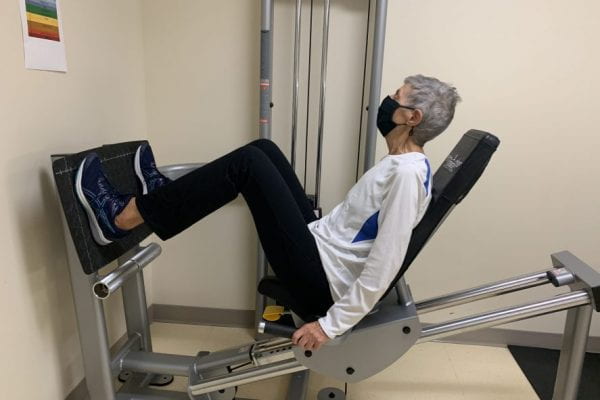
Starting a Testosterone and Exercise Program after Hip Injury (STEP-HI) was conducted between 2017 and 2024. The study tested several strategies aimed at improving muscle strength, balance, walking ability and quality of life in older women with a recent hip fracture. The strategies tested included resistance exercise (with weights) and hormone therapy with topical testosterone.
Did You Know?
Many hip fracture patients never return to their pre-fracture level of daily functioning and mobility.
What factors contribute to poor recovery after a hip fracture?
- Persistent muscle weakness
- Poor Balance
- Low mood
- Low blood levels of testosterone (a hormone present in both men and women)
Who participated?
- Women age 65 years and older
- Recent hip fracture (within 22 weeks of screening)
- Resided at home or in Assisted Living prior to the fracture and returned home after treatment or rehabilitation
- Lived within driving distance of the research center
Latest News
This study is funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) and is a collaboration of researchers from the following institutions:
- Washington University School of Medicine in St. Louis
- University of Maryland – Baltimore
- Johns Hopkins University School of Medicine- Baltimore
- University of Colorado – Denver
- The University of Texas Medical Branch – Galveston
- UConn Health – Farmington
- Hebrew SeniorLife/Harvard Medical School – Boston
- University of Utah Health – Salt Lake
- University of Pittsburgh – Pittsburgh